GIT and it's abilities
Step One - The Basics of GIT
Lets start with initializing the the project.
git init ProjectNamegit init will create a empty project on your computer.
Now you can create some file inside of the ProjectName.
Let’s create a Readme.me using VIM.
vim Readme.me
/* To insert a text press i */
Readme
=====
Hello World.
/* Hit Esc and ":wq". PS: W will save your file and Q will let you quit from VIM */Now you have created a file inside of your ProjectName directory.
Lets see what we have done with GIT. To know the file changes
git statusYou will see that Readme.md is a new file into the branch. Now we have to add this file into the repository branch.
Lets add file using command git add fileName
git add Readme.mdWe have added the Readme file but we havent added it permenantly. To do thjat we have to commit the file and add notice or short description message by using git commit -m command.
git commit -m (-m ‘Your description message’)
git commit -m 'Readme file created'Now our repository has saved in our local computer. But we’ll need web server that we can interact with other developers.
Step Two - Github.com and interaction
We already created the Git Repositry on our local computer. But we need to push the repository to the web server that someone can access and edit the file.
Easiest way to start with is using github.com. Go to www.github.com and created account.
And create empty repository.
You don’t need any extra configuration in this part if you’re following this post.
Now you have created empty reposity in github.com, also you have the reposity on your local machine. It’s time to push your local data into your github repository.
Push an existing repository
Adding a connection to your github repository
git remote add origin https://github.com/username/projectName.gitThen transmitting your filkes to the repositry
git push -u origin masterIt’ll ask your username and password.
Username for 'https://github.com': /* write your username here */
/* Hit enter then enter your password*/
Password for 'https://username@github.com': /* Enter your password then hit enter*/Now you will see the transmission progress. Counting objects .. Delta compression using up to .. Compressing object: 100% …done * [new branch] master -> master etc
Now if you go to your github repository web page, you will see your Readme.md file added.
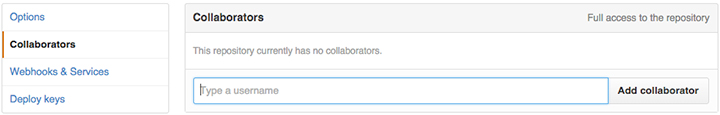
Adding a contributor to your repository
Select your repository that you want to add a collaborator into it. You’ll find settings navigatiopn on your right hand side of your repository page. Then you need to select a Collaborators menu on your left hand side.
Forking a project
Fork is like copy
